In 2021, Europe faced a concerning situation when the European Environment Agency (EEA) report revealed that air pollution caused nearly 400,000 deaths. The Impact of Air Pollution on European Mortality Rates in 2021 is undeniable, as the EEA also pointed out that air pollution can have adverse health effects and influence policy decisions on air quality. The study highlights the critical need for addressing air quality issues to mitigate the impact on public health.
Effects of air pollution on European mortality rates in 2021
The EEA’s report highlights three main air pollutants responsible for the alarming death toll in Europe in 2021.
Fine particulate matter (PM2.5), known to impact individuals with heart diseases, contributed to 253,000 deaths. Diabetes patients were exposed to nitrogen dioxide (NO2), which led to 52,000 deaths, while those with short-term exposure to ozone (O3) killed 22,000 people.
These deaths could have been mitigated if pollutants had been reduced to levels recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Health Impacts of Air Pollution in the UK
Our lungs and blood are filled with pollutants as we breathe in around 14kg of air each day. Asthma and lung cancer can be caused by exposure to air pollution.
There are hundreds of thousands of premature deaths in Europe every year due to pollutant concentrations above WHO recommendations. A report from the EEA indicates that air pollution significantly impacts deaths in Poland, Italy, and Germany, but how does the UK fare?
The vulnerability of UK residents to air pollution impacts has become a critical concern as ministers are said to ignore advice and dismantle key air quality regulations. A decision to scrap regulations raises questions about the government’s commitment to public health and the environment.
As a result of the potential exacerbation of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, as well as their impact on vulnerable populations, regulatory decisions need to be reconsidered urgently.
UK Ministers and Air Quality Regulations
A recent revelation suggests that UK ministers may have misled the public when scrapping key air quality regulations, like other European nations grappling with air pollution. Environmentalists and experts have criticized the decision to revoke regulations 9 and 10 of the National Emission Ceiling (NEC) regulations.
Before significant revisions, the revoked regulations required the development of a national air pollution control program and public consultation. Green Party MP Caroline Lucas, the Office for Environmental Protection (OEP), and others have criticized the move. Weak accountability and transparency in environmental protection could adversely affect UK citizens’ health and well-being.
Climate Change and Air Quality Interaction
The latest EEA air quality health assessment raises concerns about the failure of all 27 EU member states to meet their air quality standards, posing a threat to European health.
Climate change notably threatens air quality, particularly rising temperatures in cities. In safeguarding public health, climate change and air pollution pose complex challenges to policymakers.
Most air pollutants come from agriculture and energy consumption
The primary contributors to air pollution are agriculture and energy consumption, as the chart illustrates the percentage distribution of various air pollutants.
Explore detailed information on the sources of fine particulate matter (PM2.5), particulate matter (PM10), ammonia, sulfur dioxide, non-methane volatile organic compounds (NMVOC), and nitrogen oxides by hovering over the chart.

A holistic approach is imperative to reduce the impact of these pollutants and improve air quality.
Policy and Regulatory Framework
EU air pollution measures have been in place since the 1980s, resulting in significant reductions in emissions.
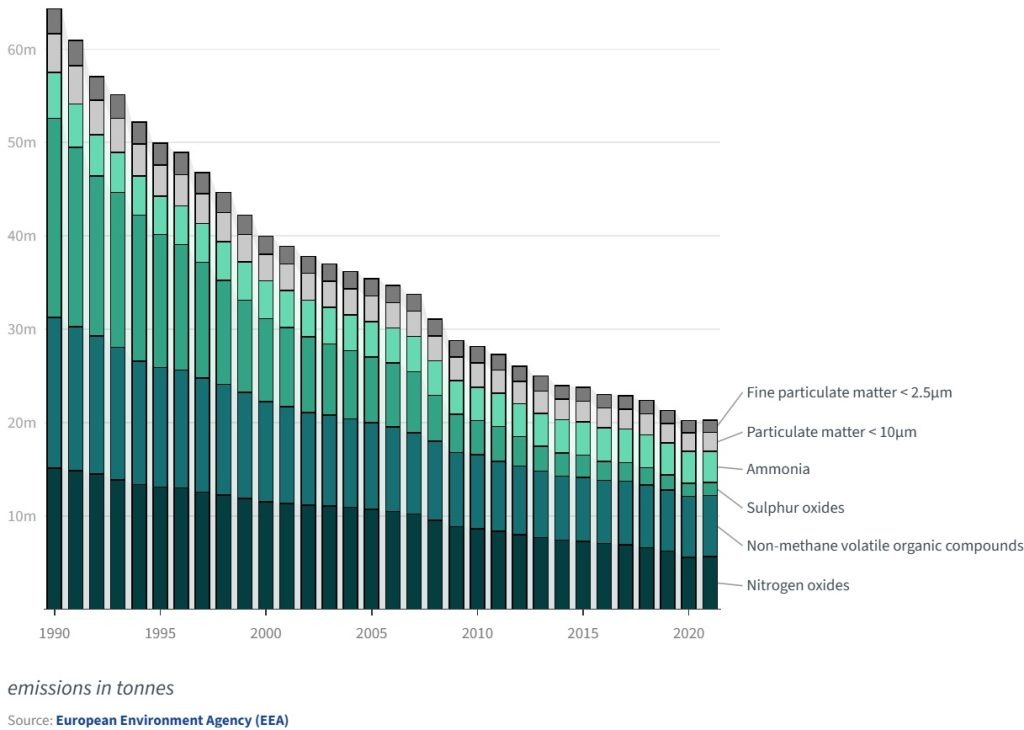
The evolution of six main air pollutants between 1990 and 2021: PM10, PM2.5, ammonia, sulfur oxides, non-methane volatile organic compounds, and nitrogen oxides
Europe still struggles with persistently high levels of air pollution despite significant declines in emissions since the 1990s.
In 2021, 97% of the EU’s urban population was exposed to PM2.5 concentrations above WHO guidelines. As a result of the burning of solid fuels for domestic heating and industrial use, central and eastern Europe and Italy had the highest concentrations of particulate matter.
The Zero Pollution Action Plan sets ambitious targets for 2030 to reduce premature deaths from PM2.5 exposure by 55%.
While there has been a 45% reduction in such deaths in the EU-27 by 2020, additional measures are essential to meet the 2030 goals and achieve the long-term vision of air pollution levels no longer deemed harmful.
A Call to Action for Public Health
It is alarming to know that air pollution remains the highest environmental health risk in Europe, even though there has been a decline in air pollution emissions over the past two decades. The silent killer lurking in the air demands urgent attention and decisive action. According to the European Environment Agency (EEA) report, in 2021, 253,000 premature deaths and 52,000 premature deaths were attributed to fine particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide exposures above WHO recommendations. Sadly, air pollution has a disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations, including lower socio-economic groups, children, and the elderly, causing over 1,200 deaths of people under the age of 18.
The United Kingdom’s situation is a cautionary tale, highlighting the delicate balance between economic considerations and public health. As Europe moves towards cleaner air, it is essential to prioritize the well-being of its citizens, particularly the most vulnerable. A commitment to sustainable practices, cleaner energy sources, and robust regulatory frameworks is necessary to mitigate the impacts of air pollution.

